There are few things in marketing we know for certain.
Show a landing page to a panel of experts and ask what’s wrong—and everyone having an answer is one of them.
While there is often no shortage of opinions on how to improve a landing page, the question remains how valuable is most of the feedback?
Even if the panel consists of experts, opinions still aren’t worth the weight of in-depth research.
On-page surveys, however, can be incredibly useful in unlocking insights for conversion optimization.
Table of contents
- On-Site surveys defined
- Using on-site surveys to remove friction, increase conversions
- Before anything else, define your objectives
- When to pop the question?
- Which questions should you ask?
- How to get more people to respond
- Mind your cognitive biases
- Using on-page surveys: A swimsuit case study
- On-Site survey tools
- Conclusion
On-Site surveys defined
Some time ago, I wrote an article on customer surveys. While both on-site and customer surveys are under the broad category of ‘qualitative research,’ the former is significantly different in their goals and execution.
While customer surveys ask questions from people who bought something from your site, you can use on-page web surveys to ask questions to a variety of different segments of visitors who use your website.
In conversion research, the main goal is the same for both types of surveys — you’re trying to identify sources of friction. On-page surveys are useful because you’re getting real-time feedback as visitors are experiencing your site.
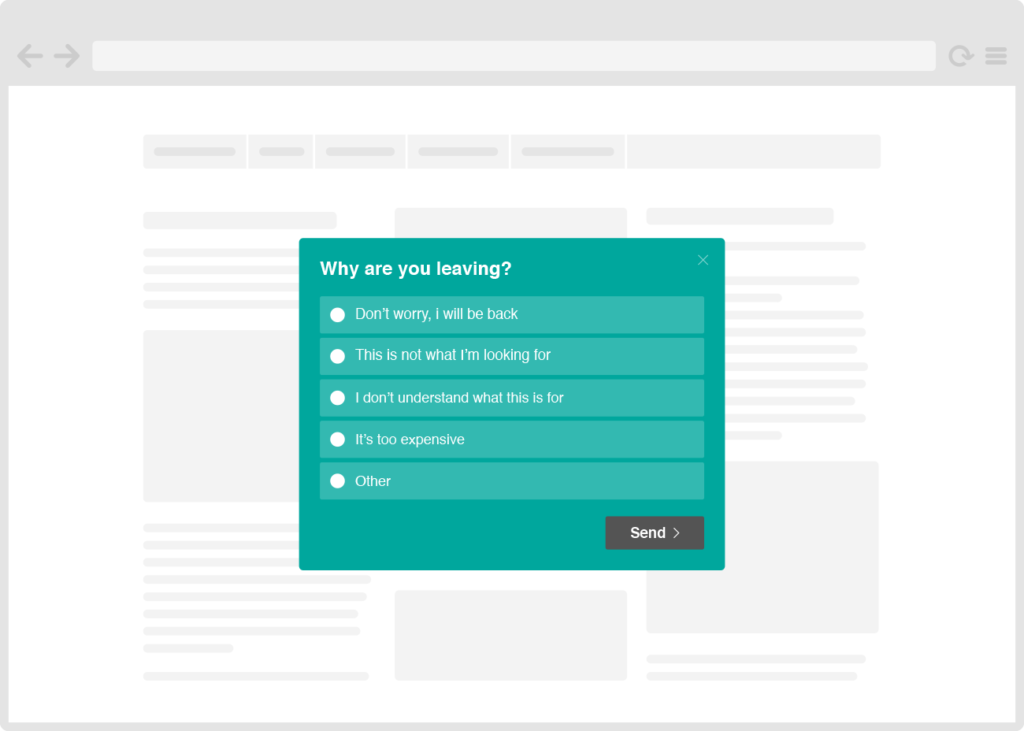
Web & exit surveys are a kind of pop-up box that appears to the visitor based on certain rules—like time spent on site, the number of pages visited, activity (e.g. moves the mouse cursor next to the browser window closing X).
This is what they look like:
What can you learn with on-site surveys?
You can learn a lot from on-site surveys. For instance, you can:
- Identify the demand for new products or improvements to existing products.
- Figure out who the customer is to help define accurate customer personas.
- Uncover UX issues;
- Locate process bottlenecks;
- Understand the root causes of abandonment;
- Distinguish visitor segments whose different motivations for similar on-site activity are undetected by analytics;
- Decipher what their intent is. What are they trying to achieve?;
- Find out how they shop (comparison to competitors, which benefits they are looking for, and the language they use, etc).
What fears do they have about handing over their credit card number? What doubts do they have about your product or service? What’s stopping them from buying—emotionally, functionally, or otherwise?
Note: there are other things you can learn from on-site surveys, of course, like NPS. There are tons of good articles on those other purposes, so we’ll just focus on the conversion research side of things.
Using on-site surveys to remove friction, increase conversions
On-site surveys are critical for conversion research. Here’s how Dustin Drees, optimization consultant, put it:

Dustin Drees:
“On-page surveys are great for in-the-moment feedback, which means they’re well suited for pages in your conversion path that underperform. What are the key pages on your site with a high exit percentage? What questions do you need to ask to understand why visitors are dropping off on these pages? You can use these insights to inform your test hypotheses later.”
Take, for example, this case study that Optimizely wrote up on Teespring. Teespring collected qualitative feedback in various ways, including customer surveys, live chat, and on-site surveys.
Through their research, they discovered that credibility was an issue. Because Teespring has an unconventional commerce model (they only ship the shirts once the minimum order size is hit), they needed to establish trust.
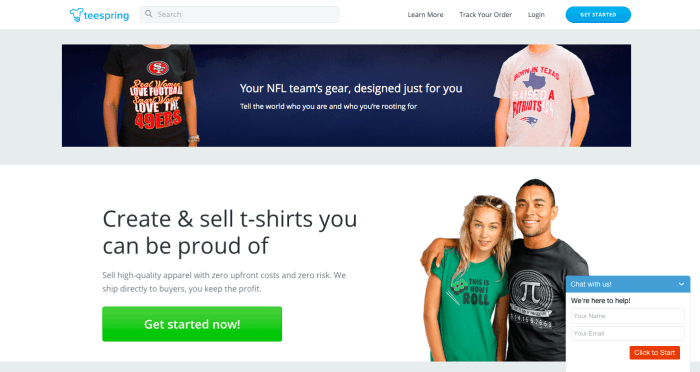
In their research, they heard anecdotes like: “Not sure if I should give my credit card information,” and, “Not sure if I’ll get my shirt.”
With this in mind, the team set up a test between two CTAs. The original:
And the variation:
The subtle change in microcopy ended up increasing conversions by an impressive 12.7%. Not bad for changing a single line of copy.
Voice of customer research using on-site surveys
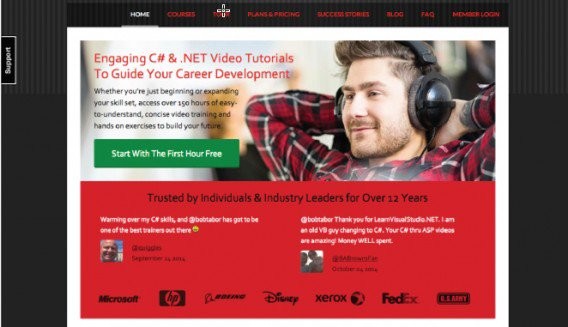
Another inspiring example comes from our own blog— a case study by Jen Havice and Dustin Drees.
In doing conversion research for LearnVisualStudio.NET, they discovered that a vast amount (almost 2/3) of respondents considered themselves beginners, and 69.74% of respondents said they were “most interested in finding their first developer job.”
They took these insights to form a basic copy experiment. Here’s the original:
The variation:
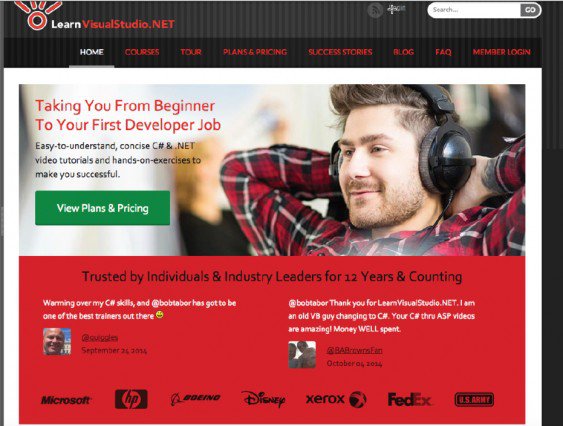
By simply telling visitors who the lessons are designed for (and where the lessons will get them), conversions increased on the Courses (+9.2%), Plans and Pricing (+24%), and Curriculum (+23.9%).
They then dug deeper into the survey responses and made a few more changes (below the fold copy, CTA, headline, etc.) Their variation ended up outperforming the original on the main call to action button above the fold by 66.3%. All primarily fueled by VOC insights from on-site surveys.
Before anything else, define your objectives
The effectiveness of your on-site survey strategy hinges on clearly defined business objectives. Otherwise, you’re just wasting your time.
What goals do you want to achieve? Be specific.
As HotJar puts it: “Before you start picking survey questions (and we’ll have you covered in just a few paragraphs), think critically about what you want to accomplish and where the best place to ask your questions may be:
- What pages are crucial to your business?
- Which over- or under-performing page(s) could most benefit from additional insight?
- Where in the conversion funnel have you spotted a leak that needs investigating?”
To ask the right questions, you need to decide what kind of data you are interested in collecting and what you will do with it. If you are not planning on acting on any of the answers, then all the effort (yours and your customers’) is wasted.
Dustin Drees factually considers a lack of clear focus as the largest mistake you can make with on-page surveys. Starting with no clear goal compounds the inefficiency of the surveys:

Dustin Drees:
“This is the biggest mistake I see people making with on-page surveys is not having a clear focus on what knowledge they’re seeking with their research. This is a problem because it will create the more common mistakes; asking questions that are too broad in their scope to lead to actionable insights, presenting questions at the wrong time, over-surveying by asking the same question on every page, or asking the wrong questions completely.
Have a clear focus on the reasons for running your survey, so you can identify the right visitors to ask, in the right spots and at the right time.”
When to pop the question?
Since you can target when and to whom you’re showing the on-site survey, keep in mind two things when deciding:
- Qualifying the visitor (is this a random visitor or someone that is considering purchasing?)
- Asking the right question at the right time (e.g. if you ask someone why they didn’t buy right when they land at the site, there will be lots of friction and confusion, and zero insight gained).
Look at your average time on site and page views per person metrics: ask questions from people who have above average engagement (for qualification reasons).
One heuristic to follow is to target people just above the average engagement. That way, you’re getting users at least in consideration of a purchase.
Ask the right question on the right page. Don’t ask, “why are you here today?” during the checkout. You get the idea.
Which questions should you ask?
Avinash Kaushik once wrote about the “three greatest survey questions ever.” The story is that, when asked which analytics tool he’d recommend to a VP on a short time frame, he answered that she should not install an analytics tool. Instead, install an on-site survey and ask these three questions:
- What is the purpose of your visit to our website today?
- Were you able to complete your task today?
- If you were not able to complete your task today, why not?
He then explained more about web survey strategy in another article, explaining that the greatest wisdom is to be gained from open-ended questions:

Avinash Kaushik
“Any good survey consists of most questions that respondents rate on a scale and sometimes a question or two that is open ended. This leads to a proportional amount of attention to be paid during analysis on computing Averages and Medians and Totals. The greatest nuggets of insights are in open ended questions because it is Voice of the Customer speaking directly to you (not cookies and shopper_ids but customers).
Questions such as: What task were you not able to complete today on our website? If you came to purchase but did not, why not?
Use the quantitative analysis to find pockets of “customer discontent”, but read the open ended responses to add color to the numbers. Remember your Director’s and VP’s can argue with numbers and brush them aside, but few can ignore the actual words of our customers. Deploy this weapon.”
That said, depending on your strategy, there are many more questions that can bring insight than those three. Think about trying to answer two categories of questions, in general:
- Why did they come to the site? Does our site match their needs? If not, are we attracting the wrong traffic? Or is there an opportunity here we aren’t capitalizing upon?
- What are the sources of friction? This is more specific that “why they didn’t buy” (understanding that is our main objective, but we have many goals to understand the big picture).
Examples of questions to ask
Here are some example questions you could ask (feel free to tweak the wording as necessary):
- What’s the purpose of your visit today?
- Why are you here today?
- Were you able to find the information you were looking for? This can identify missing information on the site—best asked on product pages.
- What made you not complete the purchase today?
- Is there anything holding you back from completing a purchase? This helps you further identify any friction.
- Do you have any questions you haven’t been able to find answers to? Y/N
- Were you able to complete your tasks on this website today? If the answer is no, allow your visitor to expand on the reason why.
There are so many different questions you could ask and get actionable insights; it all depends on your strategic goals.
How to get more people to respond
There’s no single magic question that resonates with every audience, so you’ll have to experiment.
Typically, though, there are two ways you can go about setting up your on-site survey:
- Ask a single open-ended question.
- Ask a simple yes/no question, and ask for an explanation once they’ve answered it.
The second often almost always works the best for us. As for why that is, it’s probably because of a psychological principle known as “commitment/consistency” (remember Cialdini?)
Once the user starts on the path by answering the easier Y/N question, they are compelled to continue by following up with an explanation.
Here we asked two questions that got almost the same amount of views, but one got significantly more responses:
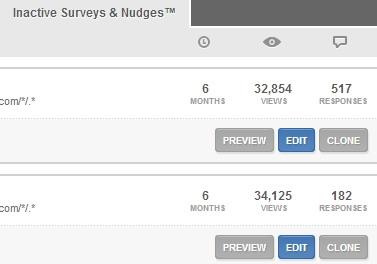
What was the difference?
- Winning question (517) responses: Do you have any questions you haven’t been able to find answers to? Y/N
- “Losing” question (182) responses: Is there anything holding you back from making a booking? Y/N
The lesson is simple: you need to experiment with different wordings. Some work better than others with specific audiences.
Here’s another example. We asked the following three questions:
- Why didn’t you complete a purchase today?
- Is there anything holding you back from making a purchase today?
- Do you have any questions you haven’t been able to find answers to?
Can you guess which question yielded which result? The results are below (pay attention to views/responses ratio):
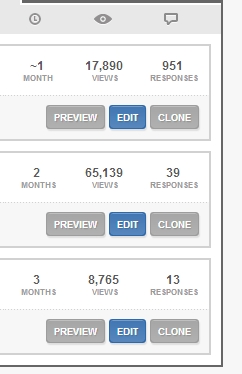
The first question performed overwhelmingly better than others. Which questions lined up with which results?
- The first question (winner) was “Is there anything holding you back from making a purchase today?”
- Second question was “Do you have any questions you haven’t been able to find answers to?” (worst performer).
- Last one: “Why didn’t you complete a purchase today?”
The takeaway? There are no universal questions that will resonate with all audiences. Our previous winning question performed worst on this audience. Keep experimenting.
Sometimes small changes to phrases can have a big difference on response rate. For instance, Groove changed their question from “why did you cancel?” to “what made you cancel?” and got nearly double the responses.
No one can know for sure why the increase occurred, but the theory is it was because the former was accusatory and put the customer on the defensive. Either way, small changes can be big increases sometimes.
Mind your cognitive biases
Just as customer surveys are susceptible to cognitive biases, on-page surveys are as well. Actually cognitive bias can strike easily on both parts of the on-page survey process: creating the survey and analyzing the results.
For example, confirmation bias causes you to overtly focus on responses that back up what you already think (and you ignore all those that say otherwise). Dustin Drees points out how to avoid some of the common blind spots:

Dustin Drees:
“Confirmation bias is always a present risk, as early as deciding what survey you want to run, as well as how and what you ask your site visitors. It is hard to avoid preconceptions of what you expect to be wrong with a page, which can skew your questions and lead you to miss signals in the responses. Before running your survey, have someone not invested in the outcome review your questions.
When analyzing the results, remember that the visitors who participated also inevitably had to choose to participate, which means they don’t represent your entire audience, but only a segment of your audience. This is called voluntary response bias. It is nearly impossible to avoid this bias, but you can minimize the effect of it by being sure you’re asking questions of visitors in only certain moments; asking questions of repeat visitors for instance can be more reliable than asking questions to every site visitor, or presenting your survey at key bottlenecks in your conversion path.”
Using on-page surveys: A swimsuit case study
Ecommerce agency, Growth Rock, had a client who sold plus-sized swimsuits for women. One of their first tasks was to help improve the product pages.
While sending a customer survey via email was considered, they ultimately decided to use on-page surveys to avoid emailing the client’s customers too much.
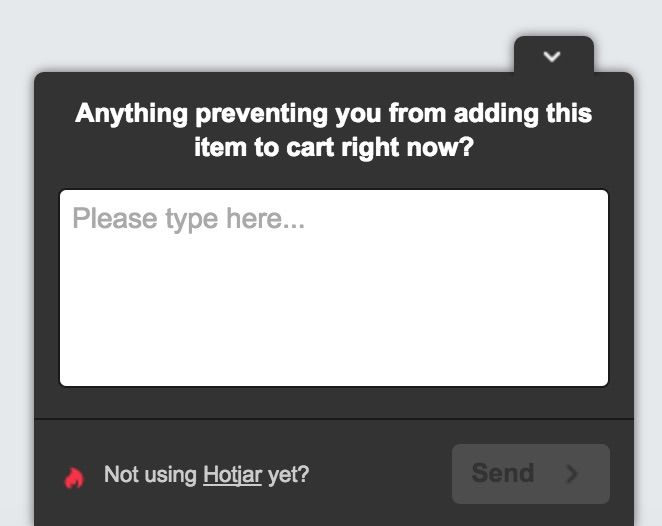
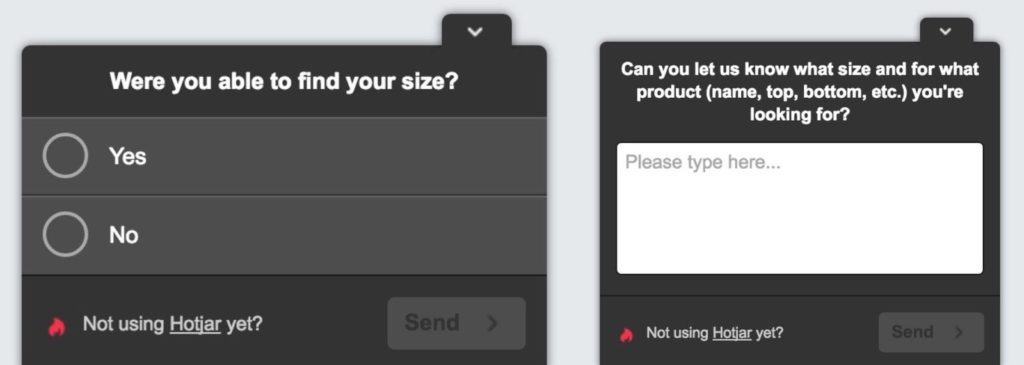
Using the tool Hotjar they asked:
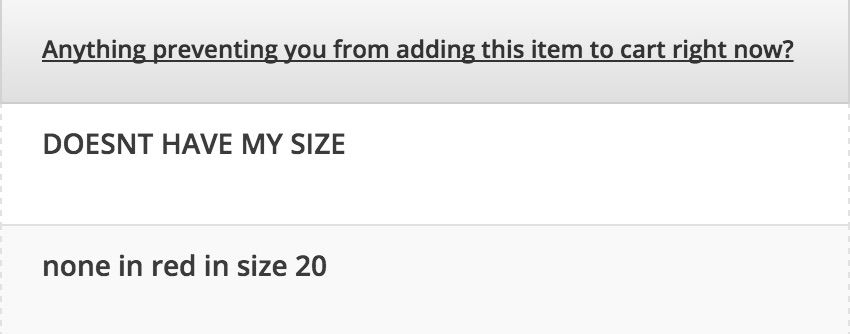
And the initial responses were revealing:
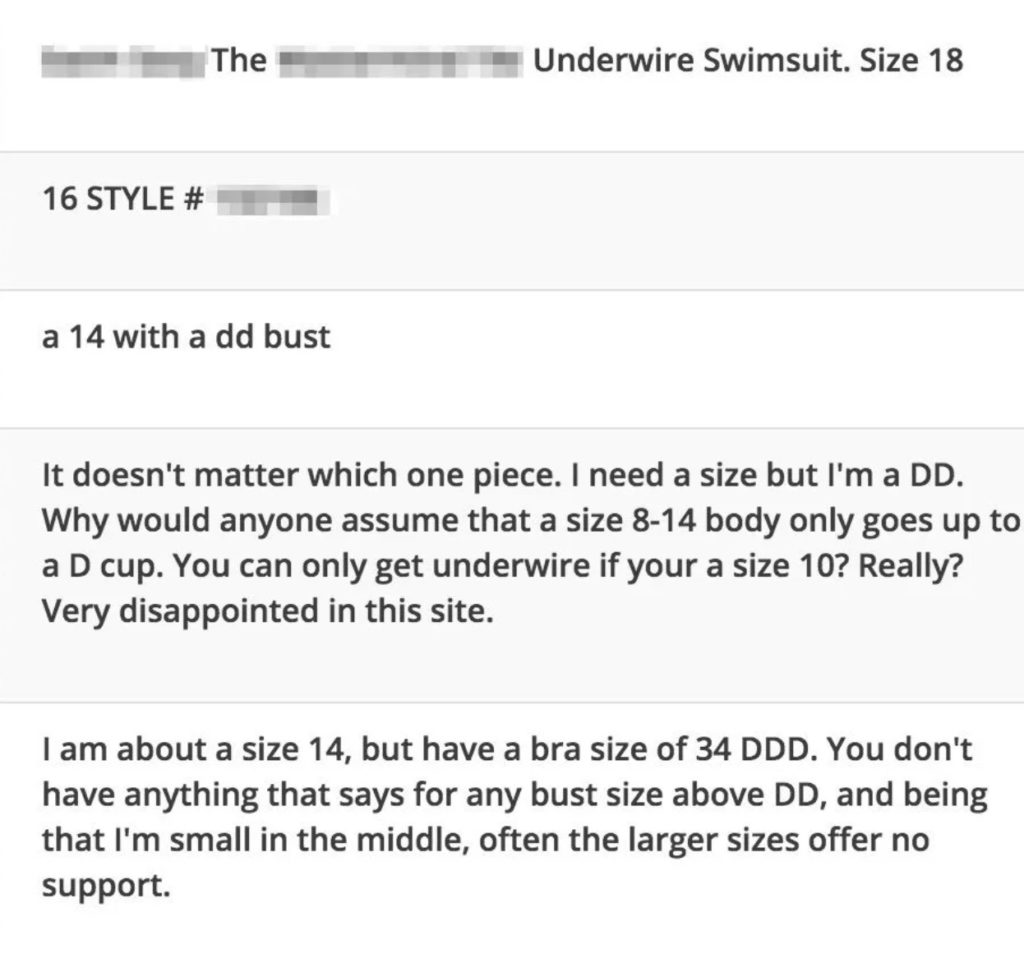
As shared on Grow and Convert, they were incredibly surprised at the results, “Hold the phone. They don’t have enough sizes? This is a plus size swimsuits site, the right size selection is a core part of the value proposition.
Obviously, that’s not a UI/UX issue, it’s a merchandizing issue. So it’s not something we can “fix” with an AB test, but it’s incredibly insightful.”
But they didn’t stop there. They decided to take their learnings one step further by asking a few additional questions.
And yet again the responses were incredibly valuable.
A few strategic questions were able to uncover issues that would have never been solved through an A/B test.
On-Site survey tools
The tool should be a secondary consideration to your strategy. Still, there are some options when it comes to tools (or read our huge conversion optimization tools guide, all reviewed by experts)
Conclusion
On-site surveys are a critical piece in the conversion research puzzle. They help you identify and remove friction from the purchasing process, and increase conversion rate in the process.
Because you’re polling traffic, and because of advanced targeting and segmenting capabilities of polling tools, you can do a lot of different things with on-site surveys.
But, make no mistake: just throwing up a HotJar exit survey with a random question does you no good at all. You must have a very clear goal in mind with your qualitative research, a goal that will inform your execution of the surveys. In addition, keep these ideas in mind:
- Ask the right question at the right time (important!)
- Experiment to maximize response rate;
- Mitigate cognitive biases;
- Make sure your on-site surveys fit into and inform the rest of your conversion research efforts.






Indeed, an on-site survey is the best way to get customers’ feedback for conversion assessment. I agree that one should have a clear goal in mind before formulation questions. Right questions will lead to the answers you need for evaluation. The great advantage is, in less time, you get answers that are ready for analysis that would help in designing a for a higher conversion rate.
Thanks,
Carl Ocab
http://www.carlocab.com
Thanks for the comment, Carl. Glad you enjoyed the article!
Hi,
thanks for the information.
A little ‘secret’ tip for on-site survey tools is:
http://survicate.com/
When I evaluated our needs (especially in terms of precise targeting conditions and not too show too much surveys to the individual user) this service was the only one to fit our needs…
Bye
Sven
Hi Sven,
Thanks a lot for this comment! It really made our day at the office.
Cheers
Kamil