Sales and marketing misalignment reduces revenue, lowers the quality of customer service, and can even dampen company culture. So how do you get aligned?
This post, based on our experiences, covers:
- What misalignment looks like—and what it costs;
- What alignment looks like—and what you get;
- Four steps to go from wherever you are now to greater alignment.
Table of contents
What misalignment looks like—and what it costs
According to The B2B Lead, sales reps spend about 50% of their time prospecting unproductive deals—while missing 80% of the most qualified leads. Not an optimal use of time.
Of course, it isn’t just your sales team that suffers. Marketing often works hard on positioning and other marketing initiatives that the sales team undervalues.
As Douglas Karr explains it:
An analogy I’ve used for quite a while with marketing is fishing. If you’re a sales driven organization, you just want to get out on the water and throw your lure. The more rods you have and the faster you can get them all in the water, the greater the chances that something will bite.
The problem is that the fish may not be where your boat is, may not like the bait you’re using, and as productive as you are—you may come home empty-handed.
How can you tell if your marketing and sales teams are misaligned?
- Your sales team repeatedly voices their frustration at “low quality” leads.
- Your sales reps disqualify a large percentage of MQLs right off the bat.
- Despite an increase in ad spend and marketing budget, customers aren’t engaging with your ads, content, and emails.
- Marketing collateral and educational resources go unused by your sales team.
- Your marketing and sales team operate independently much of the time.
One of the most common reasons for marketing and sales to be out of sync is that the customer journey is too segmented between teams. Any stage at the edge of either team’s responsibility lacks accountability (but not finger-pointing).
“There’s a blurring of what marketing is responsible for, and what sales is responsible for [. . .] and we do need to align marketing and sales around a common view of the entire funnel,” says advisor of LoopVOC, Jill Rowley.
Clarifying those responsibilities is lucrative.
What alignment looks like—and what you get
When sales and marketing are aligned, good things happen. According to research by SiriusDecisions:
- Annual company revenue increases by 8.2%.
- Brand awareness increases by 8.0%.
- Average deal size increases by 6.1%.
Alignment starts with clear communication, a focus for Josh Normand, VP of Strategic Sales at Hootsuite:
We over-communicate at multiple levels, not meeting for the sake of meetings—we’re very respectful of people’s time. There’s an agenda. Everyone has clear roles and responsibilities.
Strong communication within teams yields consistent communication to customers. When Dell needed to align marketing content with the sales team’s lead nurturing, they organized content in automation tools to keep sales and marketing on the same page.
Instead of traditional sales emails, Dell developed interchangeable content blocks based on customer interests. Contacts entered into the lead-nurturing program based on digital activity (usually visits to certain pages on Dell.com).
The sales team saw this solution as sales enablement—ongoing nurturing of not-ready prospects. That collaboration worked for Dell, with the aligned lead-nurturing program delivering a 35% higher average order value for nurtured contacts versus non-nurtured contacts.
ZoomInfo solved misalignment by creating a service-level agreement that required a dedicated member of their sales team to call MQLs:
ZoomInfo had long struggled with warm MQLs. We tried giving them to our sales development team, then tried our special sales SWAT team. No matter what we tried, we couldn’t get the conversion rate above 4%.
To align our sales and marketing teams, ZoomInfo created a sales role 100% dedicated to calling warm marketing-qualified leads. (Yes, calling them.)
Our conversion rate went from that stubborn 4% to 15%! We found the sweet spot 150 dials (yes, dials) per day.
Your company may do just fine by scheduling a weekly meeting between key members of marketing and sales. Or you may need that SLA to make it happen.
Here’s the process for figuring out what you need to do, and how to do it.
4 critical steps to align marketing and sales
Your sales and marketing alignment should center on four priority steps:
- Define and understand your target audience.
- Create core messages to speak to your target audience.
- Define shared terms and internal language.
- Create a process for working with leads.
It starts by getting everyone focused on the same audience—potential buyers.
1. Define and understand your target audience.
“Spray and pray” marketing results in messages that go unnoticed (or even blocked) by consumers. It’s marketing without a target audience. For marketing and sales alignment, both groups need to have a common target audience—one that buys products, not just shares blog posts.
“In sales, the rubber meets the road with revenue, not with likes, and favorites, and retweets, and popularity stats. It’s all about building a pipeline to revenue,” says Rowley.
To define your target audience, consider a few resources:
- Firmographic data;
- Source information;
- Customer behavior.
Firmographic data is a set of characteristics related to companies that, together, form market segments. Firmographics give deeper insights for B2B marketing teams to target accounts that get the most benefit from their products or services.
Firmographic data forces you to answer questions like:
- Who is the lead?
- Where do they work?
- What is their position?
- What is their professional background?
InsideView recommends adding a few questions to ensure your firmographic data is reliable:
- Companies pivot, are reorganized, or get acquired. How often is company firmographic and industry data updated?
- Webforms are usually short, and people sometimes enter incorrect information. Do inbound leads get their emails validated and firmographic data appended?
- Much research has shown that B2B data decays quickly. What’s the average age of our contact/account records?
- How often do we formally clean our CRM data?
- Are we doing anything to capture buying intent signals and can we overlay that with ICP to prioritize leads?
Source information tells you:
- How your largest audience finds you. Why do more people from that source come to you? What types of people are in that group?
- What people are interested in. Are they coming from competitor pages or looking up broader, top-of-funnel information?
At ActiveCampaign, for example, if someone comes from a competitive review site like G2, we can assume that they generally know what our product is but that they’re also comparison shopping.
How we interact and engage with people in this group is different than somebody who may have come in through a branded search, which allows us to deploy our sales resources more effectively.
Customer behavior analyzes what users do—the site content or emails they interact with—to help tell sales and marketing teams exactly how good (or bad) of a lead they are.
- A person who visits a pricing page likely has high interest—they aren’t just looking at what a product does, they’re thinking about spending money.
- A person who created a trial is likely more qualified than someone who hasn’t. They’ve moved beyond awareness and are interacting with your product.
With an agreed-upon target audience, you can dig into what those people need to hear from first interaction to final sales call.
2. Create core messages to speak to your target audience.
Your messaging—in marketing and sales—should fall into three buckets:
- What we do;
- How we do it;
- Why we do it.
When what, how, and why are aligned, you have a filter to make it easier to make marketing and sales decisions about your core message.
The Golden Circle, introduced by Simon Sinek in 2009, is a helpful framework. Here’s how it works:
- Why: The belief or the motivation behind your business. This asks the question, “What is our purpose?”
- How: The process—actions taken to realize the why.
- What: What you offer and the result of why.
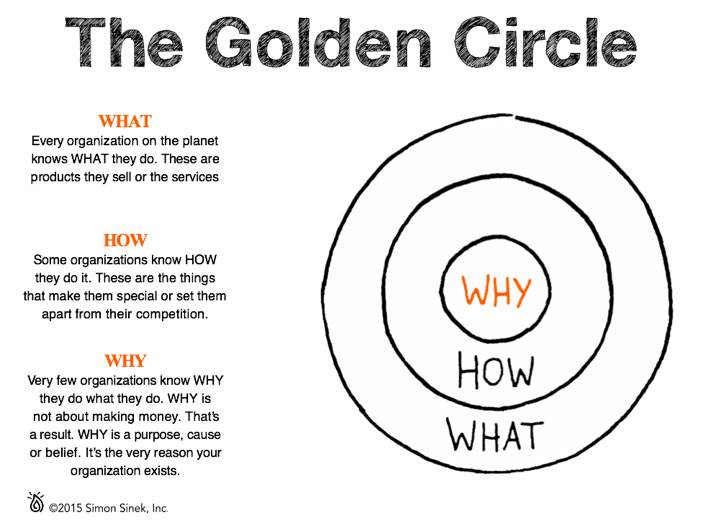
Your core messaging begins with purpose—why you do what you do. It’s your cause, what you believe, and the thought behind your every action and product. Not having a common cause as an organization is a fast track to continued misalignment.
La Marzocoo sells espresso machines. But they also run communal coffee shops. Their “why” is what coffee offers: a shared experience with friends, family, clients, or simply a good book.
Their product enriches lives, an idea central to Sinek’s description of the “why”: “to build relationships so that we enrich the lives of others.”

As Sinek says, “people don’t buy what you do, they buy why you do it.” For us, our Golden Circle approach looks like this:
- Why: We exist to help growing businesses meaningfully connect and engage with their customers.
- How: We do this by bringing together the entire customer experience, allowing these businesses to see, interpret, influence, and improve all aspects of their customers’ experiences.
- What: We do this by offering a CRM, sales automation, email marketing, messaging, and an integration layer.
Our customers don’t start off wanting a CRM; they want a way to keep track of their customers and opportunities. They don’t search for an email marketing tool; they want a way to reach their customers easily.
When you buy a product, do you think about the nuts and bolts that you’re buying? Or do you think about how you’re going to use it and what life problem it solves?
The Jobs-to-be-done framework can help you learn the job that consumers hire your product to do. But you’ve got to be willing to talk to customers. Here are a few questions you can ask:
- Why did you choose us?
- Have you referred others to us? Why?
- What alternatives, if any, did you try before us?
- If you switched from a competitor, why?
- Did any particular marketing campaign nudge you to buy?
- What is your favorite part of our product/service?
Remember, the point of customer interviews isn’t to sell anything but to understand your strengths and weaknesses.
Translate what you learn into your core messaging, which should focus on the why. Remember different audiences will have different whys, and you’ll need to address those needs consistently, with the same language, at every stage.
3. Define shared terms and internal language.
Sometimes, marketing and sales misalignment comes down to people talking about the same thing with different terminology. You may think your team is already aligned on language. But confusion is common:
- What is a lead?
- What defines an MQL?
- What defines an SQL?
In the early days of ActiveCampaign, MQL and trial were used interchangeably, which led to misunderstanding. Sometimes a trial was considered an MQL, although not all trials were actually MQLs.
After noticing frustration, a couple members of the leadership team sat down in a one-on-one meeting to talk through everyone’s understanding of term definitions and set a final, mutual definition.
Without that intervention, miscommunication could’ve caused a domino effect of problems. One team might use “lead” to describe an email capture, while another might use “lead” to describe someone on the verge of buying.
To define the terms that your marketing and sales teams use, first catalog everything you want your definitions to cover. According to the Unified Compliance Framework, there are multiple types of definitions, but two are most widely used:
- Intensional. Begins with the category, properties, or features shared by other concepts or things like it. Continues with what makes this concept or thing different than the other members of its category (e.g., “Baked goods are foods that are cooked in an oven of some fashion that uses prolonged dry heat, usually based on flour or corn.”).
- Extensional: Lists as many objects, properties, or features as necessary that represent the concept or thing being described. Explains how those objects, properties, or features fit into a more generalized category. (e.g., “Baked goods are breads, cakes, pastries, cookies, biscuits, scones and similar items of food that are cooked in an oven of some fashion.”)
Once you know who you’re trying to reach, the messages that resonate with them, and how you categorize those people internally, you can transition from research and internal discussions to consumer-facing work.
4. Create a process for working with leads.
Misalignment creates two funnels—a marketing funnel for generating pipeline and a sales funnel for closing the pipeline. When you have multiple funnels and multiple lead-nurturing processes, sales and marketing teams operate at difference paces toward different goals.
A fractured process is one of the three key challenges, the other two of which are addressed in preceding steps:
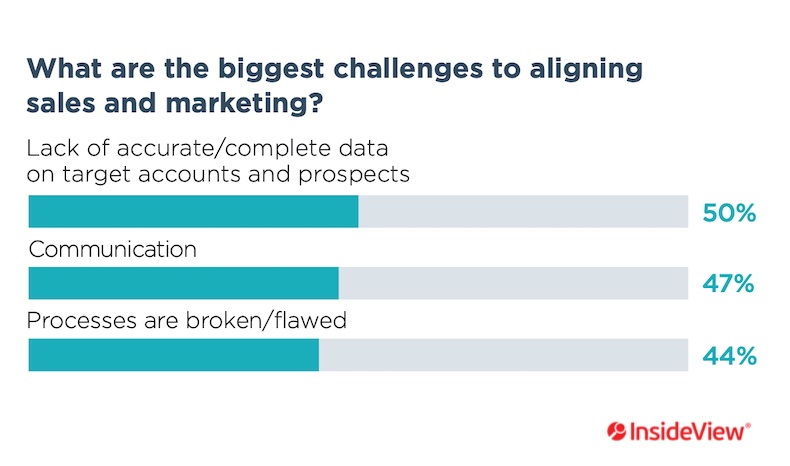
To create your process for working with leads, consider three areas:
- Routing. Where do leads go between marketing and sales? Are they tagged in a CRM or segmented in your email service provider?
- Priority. What’s the order in which you reach out to leads?
- Timing. How fast should you reach out, how many times, and over what timeframe?
At ActiveCampaign, qualified leads that fall within the target audience go to a sales representative. For leads who aren’t qualified, they stay with marketing and go into a nurturing sequence.
The higher quality a lead is—that is, the more boxes they check within the target audience—the higher priority they become.
For example, leads coming from review or comparison shopping websites are contacted within two hours, while leads coming from branded search terms are contacted within six hours. All leads are contacted four times within the first seven days of identification.
When a lead goes to a sales representative, can you automate the first outreach, or will direct human contact work best? Does this vary based on the quality of the lead? Can subsequent follow-ups be automated, and, if so, on which channels should that follow-up take place?
Remember, your customers don’t want to feel stuck in some impersonal automation loop. Consider adding personalized touch within your lead process.
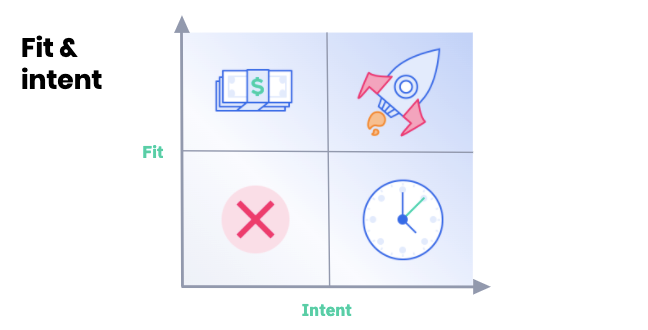
We’ve developed a “Fit & Intent” matrix to help drive decisions on engagement between sales and marketing
- Fit is how well our solution solves the needs of the customer.
- Intent is how motivated our customer or prospect is to make a change in an area we serve.
Here’s how the model works:
- Low fit/low intent leads should probably never go to sales, and marketing doesn’t need to spend much time on them. Don’t ignore these leads, but be mindful of your investment.
- High fit/high intent leads where your sales reps should move quickly with marketing offering support. These leads are the classic “don’t overthink, don’t oversell” scenario. Close the deal.
- Low fit/high intent leads may not totally match up with your target audience, but you can see if you can help them. For these leads, marketing can use educational content or collateral (such as an ebook or whitepaper) to try to push them into the high fit/high intent category.
- High fit/low intent leads are the ones you need to convert to grow your business. They might be using a competitor and fall in the middle of your target audience.
Find out where leads can fall—it might be more than one quadrant—and decide: Where does the responsibility fall on marketing? Where does the responsibility fall on sales?
Here’s the breakdown:
- Low fit, low intent: In this quadrant, there is no core ownership. This area focuses on nurturing leads, which can fall on both marketing and sales (depending on the lead source).
- High fit, high intent: A lead who falls into this quadrant is ready to buy, which means it’s time for sales to own the process and drive the conversion. Marketing is there to support sales as needed.
- Low fit, high intent: A lead in this space needs more information to see if your business can help them. The marketing team primarily owns the responsibility of this quadrant, with support from sales as needed.
- High fit, low intent: This quadrant requires joint ownership, with support from marketing and sales. This can include top-of-funnel content, sharing pricing information, or phone calls with sales representatives.
Conclusion
Sales and marketing misalignment is by no means an easy fix. That doesn’t make it any less essential.
But don’t jump straight into consumer-facing work if you haven’t yet:
- Agreed on a target audience;
- Identified the messages that resonate with them;
- Aligned on internal definitions.
Then, and only then, will your marketing and sales teams work on the same audience with the same messaging—no matter where those people are in the buying process.





Love your blog, your my new blog to follow as I just started my blog about 5 months ago and wow do I have my work cut out for me to even get 10 percent as good as you, thanks for all the shares you do.
Nice article. Thanks for mentioning the UCF, very informative.
Sales and marketing need to be aligned. After all, it’s marketing that can help bring in leads for sales to nurture. When there’s a disconnect, the company can’t thrive.
The main thing I see most people NOT doing enough of now to improve their B2B close rates is using their ‘Marketing’ systems to improve their close rates on leads after they have already responded. Almost nobody does this and can easily DOUBLE your close rates.